Leetcode problem 101 - Interval List Intersections
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
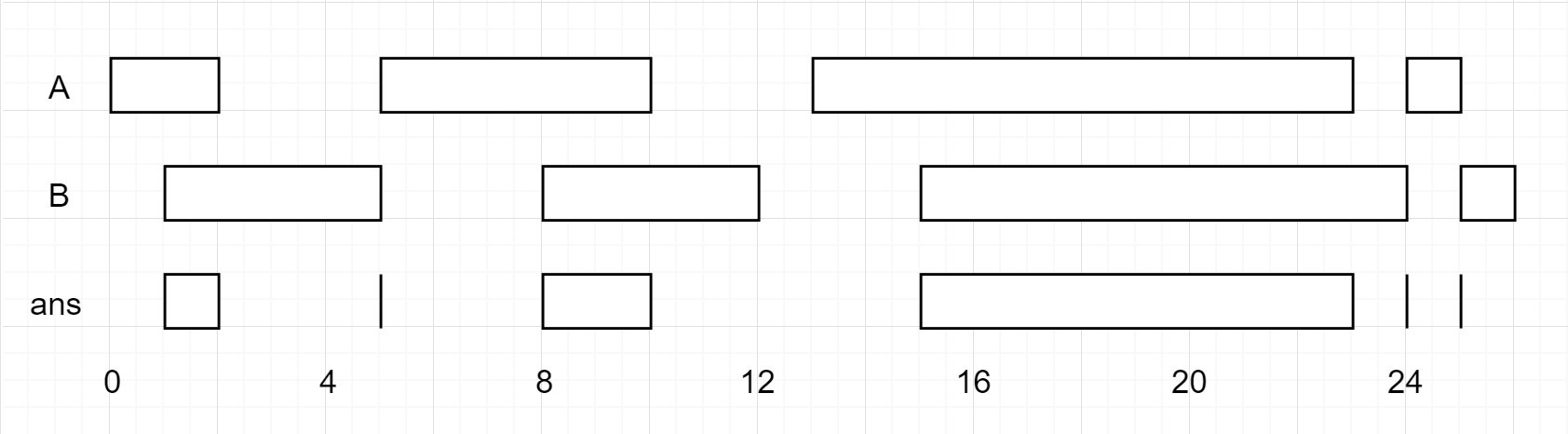 Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] Output: []
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000 firstList.length + secondList.length >= 1 0 <= starti < endi <= 109 endi < starti+1 0 <= startj < endj <= 109 endj < startj+1
/**
* @param {number[][]} firstList
* @param {number[][]} secondList
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var intervalIntersection = function (firstList, secondList) {
// Initialize an empty array to store the result of interval intersections
let result = [];
// Initialize pointers for the two lists
let firstP = 0;
let secondP = 0;
// Iterate through both lists until one of them is exhausted
while (firstP < firstList.length && secondP < secondList.length) {
// Determine the maximum starting point and minimum ending point of the current pair of intervals
let maxNum = Math.max(firstList[firstP][0], secondList[secondP][0]);
let minNum = Math.min(firstList[firstP][1], secondList[secondP][1]);
// Check if there is an intersection between the intervals (maxNum <= minNum)
if (maxNum <= minNum) {
// If there is an intersection, add the interval [maxNum, minNum] to the result
result.push([maxNum, minNum]);
}
// Move the pointer of the list with the smaller ending point to the next interval
firstList[firstP][1] < secondList[secondP][1] ? firstP++ : secondP++;
}
// Return the result containing interval intersections
return result;
};
The time complexity of this solution is O(n + m), where n is the length of the firstList and m is the length of the secondList. This is because we iterate through both lists once.
The space complexity is O(1) because we are using a constant amount of extra space to store the result array.



Leave a comment